Individual polyatomic molecules are trapped in optical tweezer arrays
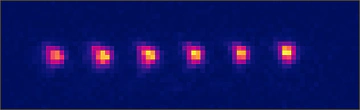
Our results on an optical tweezer array of ultracold polyatomic molecules demonstrate control of polyatomic molecules (CaOH) at the single particle, single internal quantum state level. The ability to create and manipulate tweezer arrays of polyatomic molecules paves the way for a variety of experiments harnessing the rich structure of these molecules, including quantum simulation, quantum computation, and precision studies of ultracold collisions and chemistry. Check out popular news coverage of this work in Physics World and Phys.org. Also see the Nature Research Briefing on this article.